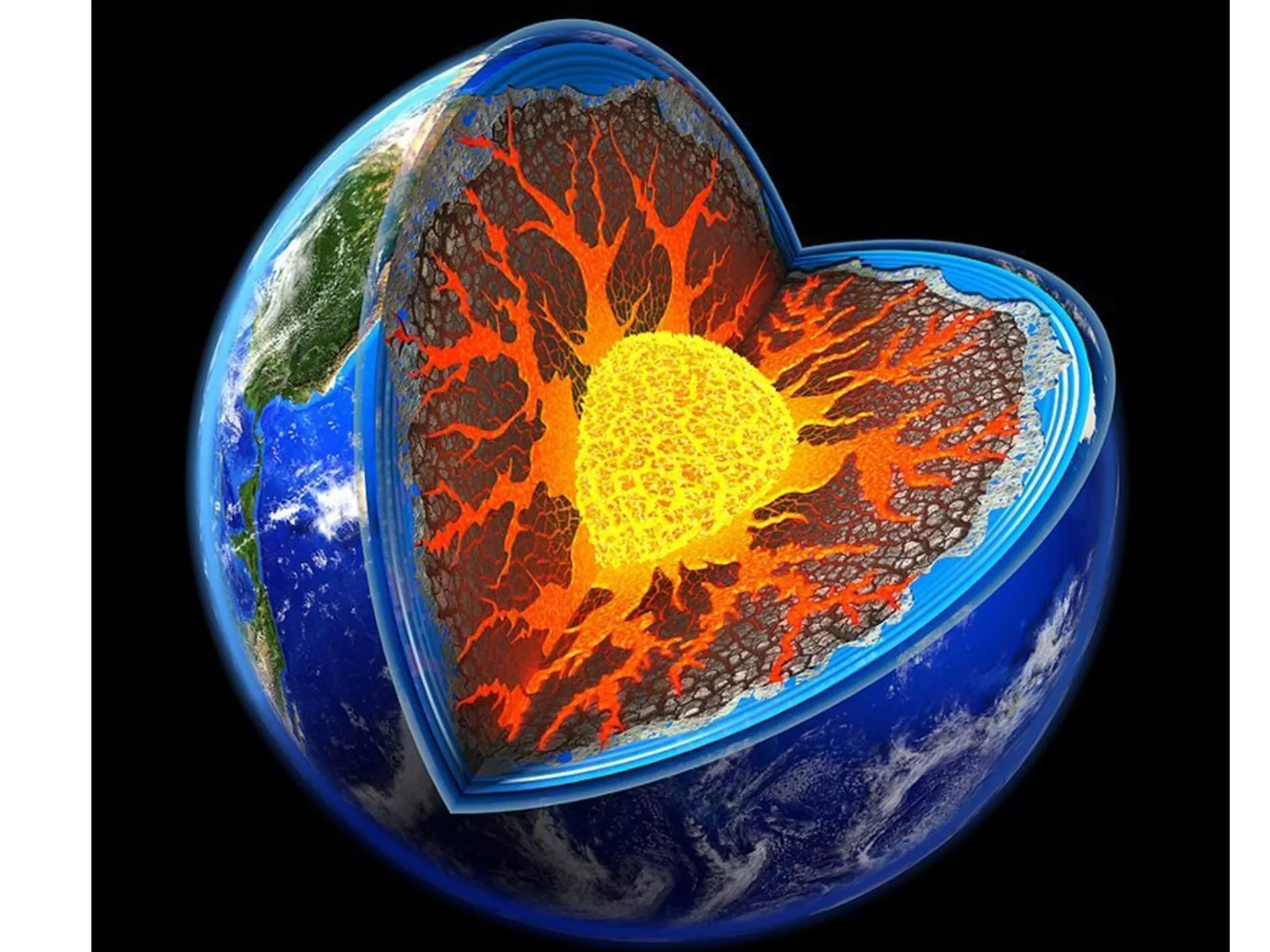
Since it is not yet possible to directly penetrate very deep into the bowels of the Earth, some indirect methods are used to study the contents of the Earth’s interior.
The study of volcanic eruptions, emissions of incandescent gases and molten rock to the surface indicates that it is very hot inside the Earth.
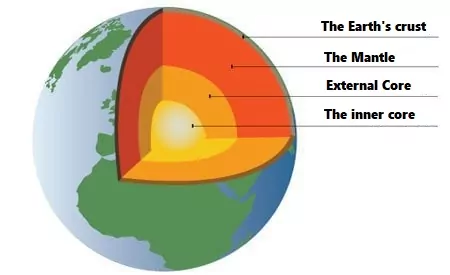
During earthquakes, waves arise, they create a kind of X-ray image of the inner parts of the Earth. What does it look like? When an earthquake occurs, different types of vibrations propagate in all directions passing through the rocks. Such waves are called seismic. Waves travel through different materials at different speeds. The direction of the waves changes when they go from one type of rock to another. When studying seismic waves with the help of very sensitive instruments, they create an assumption about what is inside the Earth.
What do we know presumably?
Today: the upper layer, a kara with a thickness of up to 48 km, consisting of solid rocks. Further at a depth of up to 2880 km is the Earth’s mantle, which also consists of hard rocks. The inner part of the Earth — the core consists of an outer liquid part (molten iron and nickel), inside which there is an inner solid metal core with a diameter of about 2560 km.
